Bonita Engine architecture
Discover Bonita Engine architecture, its APIs, main services, and how they are packaged.
Overview
The Bonita Engine is the runtime processor at the core of Bonita. It executes processes, handling actions related to tasks, such as database access, and housekeeping actions such as logging. The Engine is composed of a number of services and APIs. The services are either BPM services or generic services.
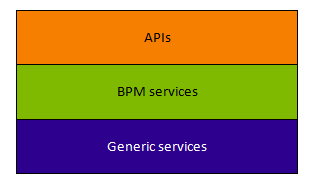
The Bonita Engine component services are completely configurable using the platform setup tool to retrieve the current configuration and update it.
Services are provided to the Engine using a ServiceAccessor. By default, this uses Spring to bind services and to retrieve service instances. The Spring configuration files are present in the classpath but beans can be added or overridden using configuration files stored in database under the CONFIGURATION table. These files are all suffixed with -custom.xml and contain Spring bean declaration examples. These files can be retrieved and updated using the platform setup tool.
Folder setup/platform_conf/[initial|current]/tenant_engine contains the following configuration files (Subscription editions only):
-
bonita-tenant-community-custom.properties: contains as comments all the available properties that can be overridden. -
bonita-tenants-custom.xml: XML file can be modified to add any Spring bean you need to add/override.
The Engine can be installed on a Java Virtual Machine (JVM), in any web/Java EE container, or can be used as a simple Java library.
APIs
This section contains a summary of the Bonita Engine APIs. For details of the APIs, the methods and related objects, see the Javadoc.
Identity API |
Manages information about an organization, that is, the set of users who can act in processes. Handles creation, modification, and deletion of organizations, groups, roles, memberships, and users. |
Organization API |
Import or export an organization. |
Process API |
Handles actions related to processes (deploy, enable, start, disable, delete), executes activities, updates process data, search for a retrieve process entities. |
Login API |
Logs in to the engine in a platform and creates a session. |
Monitoring API |
Retrieves information about current activity, such as the number of users logged in, or the number of processes currently being executed. |
Log API |
provides access to business logs, for searching and to retrieve information about current or archived processes. |
Platform command API |
Creates, starts, stops platform. |
Document API |
Manages documents that are attached to a process instance. |
Maintenance API |
Gives access to maintenance administration tasks such as enabling maintenance mode and enabling/disabling maintenance message.. |
Tenant Administration API |
Used to deploy, update and manage the BDM (Business Data Model). |
There is also a Web API, which is for internal use only, and a Command API, which is primarily for internal use.
BPM services
BPM services are related to BPM activities.
Actor mapping
Description: |
Manage mapping between actors and users, roles, and groups. |
Used by: |
- |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.actor.mapping.impl.ActorMappingServiceImpl |
Category
Description: |
Manage categories of processes. A category is a way to classify processes. Categories are handled manually by administrators in the Bonita Administrator Application and are visible to all users. |
Used by: |
Command service |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.category.impl.CategoryServiceImpl |
Notes: Store categories with the persistence service
Connector
Description: |
Execute a connector using the ConnectorDefinition: get the connector from the file system, evaluate expressions of input parameters, instantiate/execute the connector and then execute output operations. |
Used by: |
Command service |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.connector.impl.ConnectorServiceImpl |
Expression resolver
Description: |
Evaluate expressions and the associated dependencies. The expression resolver default implementation take all expressions and dependencies, flattens them and orders them by type. It then evaluate all expressions starting with expressions that are known to have no dependencies. All expressions that are evaluated at the same time have the same context of evaluation. |
Used by: |
Any service that evaluates expressions |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.expression.control.api.impl.ExpressionResolverServiceImpl |
Login
Description: |
Log in to or out of the Engine. |
Used by: |
APIs |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.login.LoginServiceImpl |
Platform login
Description: |
Log in to or out of the Engine at the platform level. |
Used by: |
APIs |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.platform.login.impl.PlatformLoginServiceImpl |
Operation
Description: |
Execute operations that update data. The Operation service can use different types of update method. The default methods, called Operators, are ASSIGNMENT, JAVA_METHOD, and XPATH_UPDATE_QUERY. |
Used by: |
Engine service, APIs when updating data using an operation |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.operation.impl.OperationServiceImpl |
Parameter
Description: |
For the Subscription editions, manage parameters of a process. Parameters are set for the scope of a process definition and are designed to be used as global configuration of a process, for example, you could store the URL of a database you use in some connectors. |
Used by: |
Engine, APIs, ExpressionService (using the contributed evaluator) when reading and updating parameters |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.parameter.propertyfile.PropertyFileParameterService |
Notes: |
Relies on Java properties in a file to store and retrieve parameters |
Process comment
Description: |
Create, update, get, list, or delete comments attached to a process instance. |
Used by: |
APIs |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.process.comment.api.impl.SCommentServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Relies on persistence service to store comments |
Process definition
Description: |
Handle process definition objects. |
Used by: |
Engine |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.process.definition.ProcessDefinitionServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Stores definition in file system and in cache using XML |
Engine
Description: |
Handles process execution. |
Used by: |
APIs when executing processes or activities |
Implementation: |
the Engine itself |
Process instance
Description: |
Handle process instance objects. |
Used by: |
Engine |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.process.instance.impl.ProcessInstanceServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Relies on the persistence service to store objects |
Generic services
Generic services perform actions that are not related to BPM but are required for successful process execution. No generic service has a dependency on a BPM service.
Archive
Description: |
Store and retrieve objects that will no longer change. For example, a process instance that is finished is archived using this service. |
Used by: |
ProcessInstance service to store ArchivedProcessInstance objects |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.archive.impl.ArchiveServiceImpl |
Authentication
Description: |
Check user credentials using a map. |
Used by: |
Login service in subscription editions |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.authentication.impl.GenericAuthenticationServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Uses the Identity service to check user credentials |
Queriable logs
Description: |
Log information related to business actions. For example, ?Activity 'step1' was created with id = 12? or ?Connector email-1.0.0 was successfully executed on activity 1547?. By default, log information is stored in a database for easy query. |
Used by: |
Any service storing objects: ?deleted activity[..]? Scheduler service: ?Job executed […]? |
Implementations: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.services.impl.SyncBusinessLoggerServiceImpl (Community edition: insert logs directly in database) org.bonitasoft.engine.log.api.impl.BatchBusinessLoggerImpl (Subscription editions: inserts all logs in batch at the end of the transaction) |
Caching in Bonita
Description: |
Store objects in the cache, and retrieve them. The service handles different caches that can be configured separately. |
Used by: |
ProcessDefinition service, Connector service, Expression service: put reusable definition objects in cache |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheService |
Notes: |
Uses EhCache to cache objects |
ClassLoader
Description: |
An abstraction layer of the classloader, making it easy to change the classloader implementation at runtime. There is a hierarchy of classloaders, with a platform classloader handling items used by the whole platform, and a process classloader for items specify to a process. Each classloader is identified by a type and an Id. |
Used by: |
Server APIs, to create and set the classloader at platform level. Engine, to handle classloader of type process |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.classloader.ClassLoaderServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Relies on the dependency service to load the jar put in dependencies for a specific classloader |
Platform command
Description: |
Register and execute platform commands. Commands are Java classes that can be executed by the engine using the API. Using this service you can create your own code to be put server side and call it from a client. |
Used by: |
API to execute platform-level commands |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.platform.command.impl.PlatformCommandServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Uses persistence service to store commands |
Connector executor
Description: |
Execute a connector: take the instantiated Connector object, set its parameters, and execute it. |
Used by: |
Connector service, to execute the instantiated connector |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.connector.impl.ConnectorExecutorImpl |
Data
Description: |
Handle DataSource objects, which describe how to retrieve and store data on an internal or external system. The Engine contains two default implementations: org.bonitasoft.engine.data.instance.DataInstanceDataSourceImpl, which handles data stored in database, and org.bonitasoft.engine.core.data.instance.impl.TransientDataInstanceDataSource, which handles data stored in memory. |
Used by: |
DataInstance service, to get the data source of a data definition to get its value |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.data.DataServiceImpl |
DataInstance
Description: |
Handle data instance objects. A data instance is a variable that has a name, a type, and a value. This service also handles expressions of type VARIABLE_TYPE. A VARIABLE_TYPE expression references a data instance. When an expression is evaluated, the value of the data instance is returned. |
Used by: |
Process API, Process executor, all services that access data |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.data.DataInstanceServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Uses the persistence service to store data instances |
Dependency
Description: |
Declare Java dependencies on business objects. These dependencies have a name and a content that is the JAR itself. For example, a process that uses an email connector has a dependency on javamail.jar that is declared at deployment. |
Used by: |
Engine, to declare process dependencies ClassloaderService, to retrieve dependencies of process |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.dependency.impl.DependencyServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Dependency information is stored in database |
Platform dependency
Description: |
Declare dependencies between entities that are related to the platform, for example, platform commands declare platform dependencies. |
Used by: |
Platform Command service, to declare dependency of platform commands |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.dependency.impl.PlatformDependencyServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Dependency information is stored in database |
Document
Description: |
Store content and properties of a document and map the document to an instance of a process. |
Used by: |
Engine APIs when retrieving documents. |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.core.document.api.impl.DocumentServiceImpl |
Notes: |
The mapping of the document is not stored in the same table as the documetn itself. |
Expression
Description: |
Evaluate an expression using the evaluator provided by another service (but do not evaluate dependencies of the expression). This service is extended by evaluators specific to the kind of expression to be evaluated. For example, in subscription editions, the ParameterService contributes an evaluator to evaluate expressions that reference a parameter. To add a new kind of expression, contribute a class implementing org.bonitasoft.engine.expression.ExpressionExecutorStrategy to the ExpressionExecutorStrategy class. |
Used by: |
ExpressionResolverService. to evaluate an expression and its dependencies |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.expression.impl.ExpressionServiceImpl |
Identity
Description: |
Handle information about elements of an organization (users, groups, roles, memberships). |
Used by: |
ProcessExecutor, to resolve actor mappings. |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.identity.impl.IdentityServiceImpl |
Incident
Description: |
Service that reports incidents to an administrator. An incident is an error that cannot be handled by the engine. The default implementation log is a file named "incidents.log" inside <CATALINA_HOME>/logs folder. |
Used by: |
Mainly by the work service. |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.incident.IncidentServiceImpl |
Job
Description: |
Handle and trace execution of internal jobs of the engine. A job is an internal action that can be triggered once or several times. (e.g. Timers are implemented using jobs.) |
Used by: |
Scheduler service. |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.scheduler.impl.JobServiceImpl, |
Lock
Description: |
Enable synchronization of code execution. The service enables creation of shared locks and exclusive locks. If a shared lock is taken out, other shared locks can also be taken out. If an exclusive lock is taken out, it blocks execution until the lock is released. |
Used by: |
ProcessExecutor, for canceling a process or for merging execution of branches |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.lock.impl.MemoryLockService |
Notes: |
Uses java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock objects that are in memory only |
Monitoring
Description: |
Monitor Engine activity, such as active transactions, active users, or JVM status. |
Used by: |
API |
Implementation: |
com.bonitasoft.engine.monitoring.impl.MonitoringServiceImpl |
Tenant Monitoring
Description: |
Provide metrics on certain services. |
Used by: |
API |
Implementation: |
com.bonitasoft.engine.monitoring.impl.TenantMonitoringServiceImpl |
Platform Monitoring
Description: |
Provide metrics on a platform. |
Used by: |
API |
Implementation: |
com.bonitasoft.engine.monitoring.impl.PlatformMonitoringServiceImpl |
Persistence
Description: |
Handle storage of objects in a persistent medium. There are two services, bonita-persistence-read for reading objects and bonita-persistence-api for reading and writing objects. The default implementation stores objects in the database, but the service could be implemented for any other type of persistent storage. The persistence service gives a unique identifier to an object. |
Used by: |
All services reading persistent objects (such as processInstanceService) use bonita-persistence-read. All services creating or modifying objects use bonita-persistence-api. |
Implementation: |
Hibernate |
Platform
Description: |
Handle creation, activation, and deletion of platform. The platform is the foundation of the Engine: creating the platform means creating database tables that are used by the Engine. |
Used by: |
- |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.platform.impl.PlatformServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Uses the persistence service to create platform. |
Profile
Description: |
Handle profiles. A profile is an entity with a name, description, and icon path that is associated with a user, group, role, or membership. A profile entity is used to determine a user’s profile (user, process manager, or administrator). |
Used by: |
API, used by Bonita Applications to modify user profiles. |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.profile.impl.ProfileServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Uses persistence service to store privileges |
Recorder
Description: |
A layer between the persistence service and all services that need to store objects. It ensures that events are triggered and that queriable log entries are written. |
Used by: |
All services storing objects. For example, the ProcessInstanceService stores a ProcessInstanceObject using the recorder Implementation: org.bonitasoft.engine.recorder.impl.RecorderImpl |
Reporting
Description: |
Handle storage, retrieval, and update of reports. |
Used by: |
API |
Implementation: |
com.bonitasoft.engine.core.reporting.ReportingServiceImpl |
Scheduler
Description: |
Handle jobs and ensure that they are executed at the required time. There are three kinds of trigger: OneShotTrigger to execute a job once only at a given time, RepeatTrigger to execute a job a finite number of times at a given interval, and CronTrigger to execute a job according to a Unix-type structure. |
Used by: |
ProcessEngine, for timers and for launching the job that matches a message event |
Implementation: |
QuartzSchedulerService, org.bonitasoft.engine.scheduler.impl.SchedulerServiceImpl |
Notes: |
Relies on Quartz to launch jobs |
Session
Description: |
Handle user sessions. A session is an object stored in memory that contains several kinds of information about the client that uses it, for example, userId, ClientIp, ExpirationDate. |
Used by: |
LoginService,SchedulerService,WorkService to create sessions |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.session.impl.SessionServiceImpl |
Platform session
Description: |
Handle platform sessions. These sessions are created when something logs in to the platform. |
Used by: |
PlatformLoginService |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.platform.session.impl.PlatformSessionServiceImpl |
Transaction
Description: |
Handles business transactions. A business transaction is a high-level transaction that contains several technical transactions. This service is compatible with JTA. |
Used by: |
Almost all services, including persistence service to register technical transactions. |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.transaction.TransactionServiceImpl |
Work
Description: |
Trigger work for immediate execution but asynchronously. Unlike the scheduler service, which uses persistent storage, the Work service stores data in memory for better performance. This means that clients of the service must handle restart if a triggered work does not complete. For example, if the JVM shuts down, when it restarts the client must check for incomplete work and re-trigger it. |
Used by: |
ProcessExecutor, to trigger work to execute flow elements one after another |
Implementation: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.work.ExecutorWorkService |
Notes: |
Trigger launches work in a ThreadPool. For Community Edition, work items are launched in sequence, each one in a new thread. For subscription editions, work items are triggered in multiple threads. |
XML
Description: |
Parse and write XML files. |
Used by: |
BusinessArchiveBuilder, to read/write process definitions ConnectorService, to read connector definition |
Implementations: |
org.bonitasoft.engine.xml.parse.SAXParser (parse using sax) |
Packaging
The Engine is provided as three .jar files:
-
bonita-common contains code that is used by both the server and client sides of the application. For example, the API interface is accessed both on the server side, which contains the API implementations, and on the client side, which has a proxy on the API. It also contains objects such as BusinessArchive, which is the JavaObject representation of a .bar file.
-
bonita-server contains code used on by the server. For example, it contains service implementations, the services accessor, and API implementations.
-
bonita-client contains client-only code. For example, it contains the Accessor service for the APIs, which is not in the common or server packages to prevent the server code calling the client-side API accessor.
|
In subscription editions, these jar files are respectively:
|