Bonita Engine API overview
Customize or add to your application by developing new connectors, actor filters or by replacing/enhancing existing services
Concepts
APIs
Bonita Engine has the following Java APIs:
Identity API |
Manages information about an organization, that is, the set of users who can act in processes. Handles creation, modification, and deletion of organizations, groups, roles, memberships, and users. |
Organization API |
Import or export an organization. |
Process API |
Handles actions related to processes (deploy, enable, start, disable, delete), executes activities, updates process data, search for a retrieve process entities. |
Login API |
Logs in to the engine in a platform and creates a session. |
Monitoring API |
Retrieves information about current activity, such as the number of users logged in, or the number of processes currently being executed. |
Log API |
provides access to business logs, for searching and to retrieve information about current or archived processes. |
Platform command API |
Creates, starts, stops platform. |
Document API |
Manages documents that are attached to a process instance. |
Maintenance API |
Gives access to maintenance administration tasks such as enabling maintenance mode and enabling/disabling maintenance message.. |
Tenant Administration API |
Used to deploy, update and manage the BDM (Business Data Model). |
There is also a Web API, which is for internal use only, and a Command API, which is primarily for internal use.
For details of the Engine APIs, the methods and related objects, see the Javadoc. Note that the APIs are the same for subscription editions, but some features are only active if the appropriate license is installed. If you try to access a feature for which you do not have a license, a Feature not active error message is returned.
There is also a high-level Web REST API, intended for customers developing applications.
API access
The Bonita Engine APIs can be accessed locally or remotely, in the following modes:
-
Local: the client accesses the server directly in local mode (both are running under the same JVM)
-
HTTP: the client accesses a remote server via HTTP
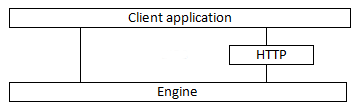
The mode you use must be specified, either in the bonita-client-custom.properties file, or programmatically (recommended way, see next section). By default, the access mode is local. This can be used when the client and engine are using the same JVM. The file contains commented out configurations for remote access modes. To change the mode, simply comment out the configuration for local and uncomment the relevant remote configuration.
There is a slight overhead in using the remote access methods, so you are recommended to use local access whenever it is possible.
Getting started with the Bonita Engine APIs
Before you run a Bonita application, configure how the application (client) accesses the Bonita Engine (server). For a HTTP access it can be done using following java code:
final Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<>();
if (HTTP.equals(apiType)) {
parameters.put("server.url", "http://localhost:8080");
//application name is the name of context, default is bonita
parameters.put("application.name", "bonita");
}
APITypeManager.setAPITypeAndParams(ApiAccessType.valueOf(apiType), parameters);All sequences of API calls start with logging in (internally, Bonita runtime creates a session) then retrieving the APIs that will be used in the application.
The APIs are retrieved using the APIClient.
The following example shows how to retrieve the log in, then retrieve the Process API for that session. Pre-requisite: the platform has already been created and initialized and the Engine is running.
// Create a new API client:
final APIClient apiClient = new APIClient();
// use it to log in:
apiClient.login(username, password);
// Then retrieve the Process API:
final ProcessAPI processAPI = apiClient.getProcessAPI();When the application has finished processing, log out to delete the session:
apiClient.logout();