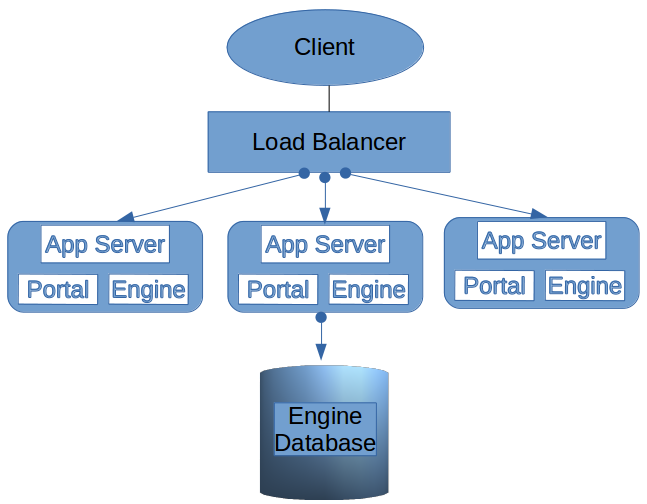
Overview of Bonita Platform in cluster
Learn how to achieve High availability by setting up Bonita Platform in cluster.
|
For Enterprise and Performance editions only. |
You can use Bonita in a cluster configuration to provide increased availability: more than one node runs Bonita Engine, so if a node becomes unavailable, the remaining nodes in the cluster can take over, minimizing the interruption to the service and therefore to your business. A Bonita cluster alone does not guarantee high availability. You must also ensure that the prerequisite infrastructure is highly available.
Introduction
The advantage of using a cluster configuration is better availability. The cost is a slightly more complicated configuration to set up and maintain. A process that already runs on Bonita will run without modification on Bonita in a cluster.
Bonita cluster characteristics:
-
High availability: Provided you have at least two active nodes and the prerequisite infrastructure is highly available, your Bonita cluster is highly available.
Differences for Bonita Applications users
The HTTP load balancer hides the fact that you are not always using the same Bonita Runtime. The exception to this is if a node fails while you are completing a form; in this case, the data you have entered might not be stored, and you will have to start filling in the form again when a new Bonita Runtime takes over.
Differences for process designers
No changes are needed to make a process run in a Bonita cluster. A process that runs in a non-cluster system will run unchanged in a cluster. However, depending on your process, some optimizations might be possible. For example, to minimize the impact on users of a failover while they are filling in forms, do not make forms too long. This is recommended good practise for all process forms, but is even more important when a process is running in a cluster.
The Bonita Studio development environment runs on a single node; there is no advantage to installing it on a cluster.
Technical description
This section describes the structure of Bonita deployed in a cluster. A cluster is a collection of nodes each running Bonita Runtime and an application server.
A Bonita cluster is a collection of at least two nodes that run Bonita Runtime and an application server. An HTTP load balancer directs the connection to one of the available Bonita nodes, balancing the workload of the nodes. If a node becomes unavailable, the load balancer redirects the connection to another node.
The Bonita Engines exchange information to enable the redirection. This means that all automatic actions handled by the Engine (including automatic tasks, events, timers, and automatic state transitions of tasks) are automatically taken over by another node.
Each Bonita Runtime works with a local Bonita Engine, so when a user logs in, they are logged in to a specific node. If that node becomes unavailable, the user session is lost. This means that any transaction that is not yet committed is lost, including any data entered in a form but not submitted. The user will need to log back into Bonita Runtime.
Assumptions: We assume that Ubuntu Linux is used as the operating system for Bonita nodes in a production system. The application server used is Tomcat.
Prerequisite infrastructure:
-
A highly available load balancer
-
A highly available network, with all nodes able to see all other nodes
-
A highly available database accessible from all nodes
-
All nodes including the database one should be configured with the same clock (via NTP time synchronization for example) and same timezone (UTC is recommended)
Definitions:
-
Load balancer: an HTTP load balancer manages the allocation of work to nodes in the cluster. No load balancer is provided with Bonita, so you can choose the most appropriate for your system. For a production system with a high load, a hardware load balancer is recommended.
-
Node: a JVM running a Tomcat application server and a Bonita Runtime. For high availability, separate physical nodes are required.
-
Engine database: a single database used by all the Bonita Engines in the cluster. It is the equivalent of the local database in a non-cluster configuration. The database needs to be highly available and to handle multiple simultaneous accesses.
-
Failover: if a node in the cluster fails, the work it was performing is redirected by the load balancer to another node in the cluster. This is known as failover, and can be automated or manual.
-
Client: a process application client. A client application connects to the cluster through the load balancer, and uses the Bonita Engine API. Even if your process users do not use Bonita Applications, it is still present in the cluster, so can be used for administration.
Limitations
The nodes must all be in the same datacenter, to keep latency of updates to shared information to an acceptable level.
All nodes must run the same exact version of the Bonita Runtime. e.g. a 7.14.2 will not be able to connect to a cluster of Bonita Runtime in 7.14.1.
The Hibernate L2 cache will be automatically disabled, leading more frequent database accesses.
The load balancer must be configured to use sticky sessions (this is needed to manage sessions created when users log into the Bonita Runtime).
Active and passive nodes
If an active node fails or is stopped, the load balancer redirects work to the remaining active nodes. This keeps the downtime to a minimum, but increases the load on the active nodes.
A passive node is installed with exactly the same software and has the same configuration as an active node, but the application server and Bonita Engine are not started. If you have a passive node in your cluster, there is no mechanism in bonita for starting that passive node if an active node goes out of service. This could be provided by a third-party application.
A passive node is a "cold standby". It does not consume computing resources.
To add a cold-standby node to the cluster, the necessary licenses must be installed, the configuration must be completed and it must be activated in the load balancer. But the application server and Bonita Engine must not be started on the passive node.
A cluster needs a minimum of two active nodes for high availability. The maximum number of nodes you can have depends on the load balancer you are using.
Advantages and drawbacks
A Bonita cluster has the following advantages over a single-node system:
-
A cluster provides high availability, as long as your entire infrastructure, including the network and database are highly available. If a node is shut down, stops, or crashes, anything that was running on that node is automatically retrieved by another running node in the cluster.
-
A new node is discovered and added to the cluster easily because of the Hazelcast in-memory data grid.
-
The network connection of a node is flexible: it can be configured with or without multicast.
-
A cluster is easy to configure.
-
BPM event matching and timer execution are distributed across the cluster by Quartz.
There are some drawbacks to the basic Bonita in a cluster configuration, but these can be addresses using other component in your infrastructure:
-
Only active-active modes is supported. There is no mechanism for starting a new node if a cluster node goes out of service. This could be provided by a third-party application.
-
There is no integrated load balancer, so the client application selects the node on which to make a API call. You should use an external load balancer. For high volume, a hardware load balancer is recommended.
-
All the nodes must use the same database, so the database itself must be highly available.
Upgrading the version of the Bonita Runtime in cluster
|
All nodes of the cluster must use the exact same version. It will not be possible to start a node on an existing cluster having a different version. |
Since all nodes must use the exact same version of the Bonita Runtime, the cluster must be shut down entirely to be able to change the version.
When only upgrade to a maintenance version of the same release you will not need to migrate the database but only upgrade the bundle or docker container:
-
Configure new bundles or docker container with the newer maintenance version
-
Stop all nodes having the previous version
-
Start nodes with the newer version one by one
When migration to a different release of the Bonita Runtime, the database also needs to be migrated. See here